A
power inverter, or
inverter, is a
power electronic device or circuitry that changes
direct current (DC) such as from batteries into
alternating current (AC). Circuits that perform the opposite function, converting AC to DC, are called
rectifiers.
What size Inverter?
Inverters typically have two ratings:
continuous watts and
surge or
peak watts.
To calculate the minimum
continuous, from your power budget add together the watts for all of the devices that might be running simultaneously.
The peak watts is how much the inverter can supply for a brief period of time. Many devices (e.g., refrigerator) will draw 4 to 10 times their continuous load when they start up; this is known as
in-rush current.
Key Features
Wave Form
There are pure sine wave inverters that produce power similar to the grid, and lower cost inverters that produce a modified wave form that works for most devices. Devices that use induction, e.g., motors or induction cook tops, will typically not work, or work poorly, with a modified wave inverter.
Efficiency
Efficiency is one Inverters key features. An 80% efficient inverter is essentially throwing 20% of your power away as heat. A quality inverter will have a high efficiency. For example, the Enphase IQ7 has an inverter efficiency of 97.6%.
Parallel
Some inverters have a feature known as paralleling. It allows a second inverter to be connected to a first to increase both the continuous and peak power available.
Inverter Types
Off Grid
These are grid-forming inverters, they set both the voltage and frequency and are probably the most common type of inverter. An off-grid inverter is for example used to provide a power to a cabin that is far from the power grid.
Grid-Tied
A grid-tied inverter matches the grid's frequency and when power is available from the DC side raises the AC voltage slightly higher than the grid's voltage. Because the AC voltage from the inverter is higher, power flows from it into the house and then out to the grid. When the grid goes down, these inverters shut down.
Some grid-tied inverters (e.g. Enphase IQ7) allow their power output to
be scaled by shifting the frequency between 60 and ~63 Hz. This provides
a power utility the ability to scale back residential production in the event
of too much power being generated and is mandatory in some areas (e.g.,
Hawaii, Peurto Rico, California). It also allows for AC Coupling so residences
an have power when the grid goes out. | 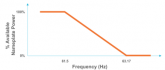 |
Hybrid
A hybrid inverter acts like a grid-tied inverter when the grid is up, but if the grid goes down is capable of acting like an off-grid inverter. Essentially it acts like AC coupled system.
Grid-Following
A grid following inverter augments another inverter trying to keep both the voltage and frequency stable. A subset of these match the phase and frequency rather than stabilize it. This is so they do not interfere with control of grid-following inverters that have been frequency adjusted to alter power output.
Will on Inverters



